Innovational Monitoring Technologies
We provide latest monitoring technologies in the field of endocrinology and diabetes such as:
- Continuous glucose monitor System (CGMS)
- Insulin Pump
- 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
- Endocrine Genetics
CGMS
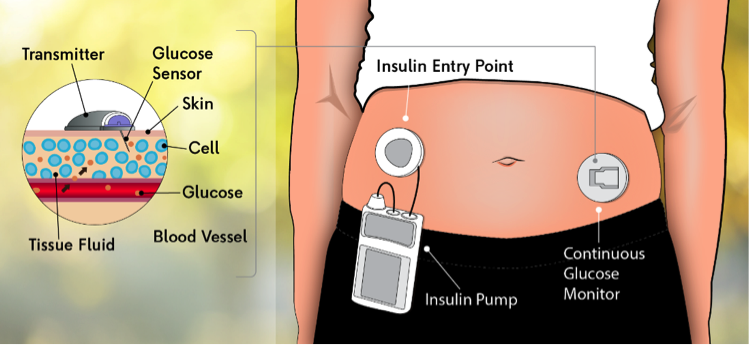
A CGMs works through a tiny sensor inserted under your skin, usually on your belly or arm. The sensor measures your interstitial glucose level, which is the glucose found in the fluid between the cells. The sensor tests glucose every few minutes. A transmitter wirelessly sends the information to a monitor.
The monitor may be part of an insulin pump or a separate device, which you might carry in a pocket or purse. Some CGMs send information directly to a smartphone or tablet.
Compared with a standard blood glucose meter, using a CGM system has the advantage of
- better management your glucose levels every day
- have fewer hypoglycaemias
- Need fewer finger prick tests
- Alarm systems for the high and the low sugars
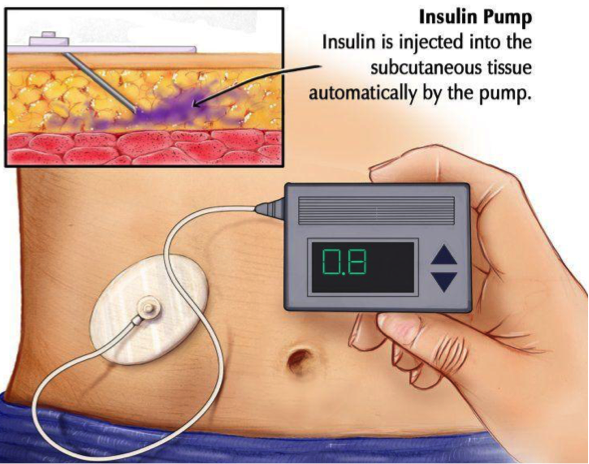
Insulin Pump
Insulin pumps are small, computerized devices that mimic the way the human pancreas works by delivering small doses of short acting insulin continuously (basal rate). The device also is used to deliver variable amounts of insulin when a meal is eaten (bolus).
The pump is attached to a thin plastic tube (an infusion set) that has a cannula (like a needle but soft) at the end through which insulin passes. This cannula is inserted under the skin, usually on the abdomen. The cannula is changed every two days.
Whether or not to use a pump is a personal decision. You can manage your diabetes equally well with pumps or multiple injections, so it comes down to your preference.
Advantages are: Better quality of life, lesser hypoglycaemias and better glucose control.
Disadvantages are: Cost of therapy, requires lot of training and motivation and finally pump is an electronic device equally vulnerable to malfunctions like others.
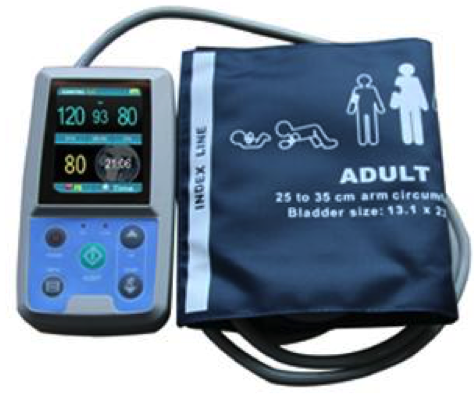
24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring allows many blood pressure (BP) readings to be recorded over a 24-hour period, whether the patient is awake or asleep.
In most cases, with ambulatory BP monitors, readings are taken every 15 to 30 minutes during the day and every hour at night. The heart rate can also be measured at the same time.
Multiple BP readings can be averaged over the 24-hour period to obtain the mean or average BP. Variations in BP and heart rate, the BP distribution pattern, and other statistics can be calculated.
It is a very useful way to detect white coat hypertension, masked hypertension, sustained hypertension, difficult to control hypertension and fainting/syncope evaluation.
Endocrine Genetics
Some endocrine genetic disorders have well known, characteristic patterns, whilst others are exceedingly rare. It is impossible to know all genetic disorders but generic clues may be useful, such as young-onset and/or aggressive disease or the development of multiple rare disorders within an individual, or one or more rare disorders within multiple family members.
Finding the problem mutation provides the opportunities of family testing and reproductive planning.
We liaison with the best service providers in the field of genetic analysis for appropriate diagnosis and genetic counselling.